|
The aim of this research line is to contribute to an early diagnosis of cardiovascular pathologies, by providing functional and quantitative information of the heart and vessels obtained from images (mainly echocardiography, magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography). Our group develops theory and methods applied mainly to: Myocardial functional analysisMyocardial ischemia can lead to movement abnormalities of myocardial regions that could be too subtle to be detected visually. We have developed analysis programs that can provide quantitative information on the myocardial movement, with the aim of identifying and characterizing abnormalities. B-spline non-rigid registration techniques have been optimized for cardiac motion detection on ultrasound, MRI and tagged-MRI sequences. Specially important has been the characterization of myocardial strain, as it is an indication of active contraction. Methodologies have been extended to three dimensions where motion can be completely characterized. The degree of irrigation of each myocardial region can be detected by images with contrast agents. Different techniques have been developed to analyze and compensate the motion of these sequences to provide quantitative information of perfusion. Both echocardiography and first pass gadolinium MR imaging data have been studied. Vascular imagingGreat and small vessel function is important to assess the prognosis and treatment of cardiovascular patients. Different tools have been designed to efficiently segment great and small vessels determining patient staging. Improving image acquisition and analysisCardiac Imaging implies important challenges in acquisition mainly due to simultaneous cardiac and respiratory motion. Allowing free-breathing acquisition has a clear impact in acquisition time and patient comfort. Motion compensation is achieved with non rigid registration techniques. Image enhancement can also be achieved using registration and multiresolution techniques, allowing improved functional assessment.
Contrast-enhanced MRI signal intensity of subendocardial tissue projected onto a 3D endocardial shell reconstruction of the left ventricle. These maps could help to identify conduction channels that are related to ventricular tachycardia |
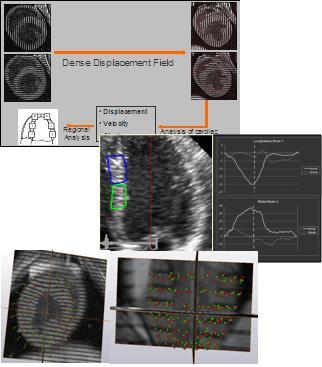
Non-rigid registration techniques optimized for cardiac motion estimation
Myocardial perfusion studied using images with contrast agents. Motion compensation is required for regional analysis
Vascular imaging: segmentation of the aorta from CT images |
A key issue of this work has been the validation of the proposed software tools with a large number of experimental and clinical images, in close contact with medical personnel, leading to established collaborations:
This material is presented to ensure timely dissemination of scholarly and technical work. Copyright and all rights therein are retained by authors or by other copyright holders. All persons copying this information are expected to adhere to the terms and constraints invoked by each copyright holder. Permission to reprint/republish this material or to reuse any copyrighted component of this work in other works must be obtained from the copyright holders.
Copyright © 2005-2020 BIT-UPM. Map of web.
Last modified on 22 Jul. 2020 by andres@die.upm.es