|
The aim of this activity is to develop image analysis
methods
that allow processing and measuring data acquired with the most recent
state-of-the-art microscopy technologies for biomedical understanding.
These technologies provide multidimensional
in-vivo observations of
organism models such as zebrafish. Thus, image analysis is
required to
approach new challenges in systems biology at the different genetic,
proteomic, cellular, organic and individual levels. Our group develops theory and methods applied mainly to: Embryogenesis reconstructionImage processing methodologies for filtering, tracking and segmentation based on mathematical morphology that allow reconstructing the cell lineage tree of zebrafish and sea-urchin embryogenesis. In-vivo (3D+T) data are acquired with 2-photon laser scanning microscopy, non-linear harmonic imaging (SHG, THG) and selective plane illumination microscopy (SPIM).Spatio-temporal gene atlas of zebrafishDevelopment of image registration and quantification methods to create a 4D atlas of gene expression domains during early zebrafish embryogenesis using in-situ hybridization techniques. The extraction of both the cellular localizations and the level of expression of different genes at different developmental stages will help the understanding of genetic regulatory networks in their spatio-temporal context.Morphogenesis modelingDefinition of high level mathematical descriptors of morphogenesis processes that fit with real observations. The quantitative characterization of the embryonic development provides measurements of similarities and differences among different individuals.Protein registrationDevelopment of image registration algorithms to automatically fit protein atomic domain models into medium-resolution 3D electron microscopy reconstructions.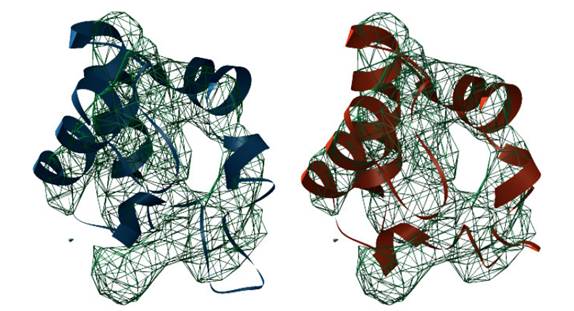
Registration of protein model from reference domain 1b7vA0 (blue) to best fitting (red) into target domain 1ls9A0 (mesh) |
Zebrafish nuclei tracking (trajectories in red) during gastrulation
Animal pole views of the zebrafish 3D Atlas where five genes were registered: gsc (red), chd (purple), spt (green), snail (blue) and atv (yellow)
Multi-scale segmentation of neural region in zebrafish embryo at 12 hours post fertilization |
This material is presented to ensure timely dissemination of scholarly and technical work. Copyright and all rights therein are retained by authors or by other copyright holders. All persons copying this information are expected to adhere to the terms and constraints invoked by each copyright holder. Permission to reprint/republish this material or to reuse any copyrighted component of this work in other works must be obtained from the copyright holders.
Copyright © 2005-2014 BIT-UPM. Map of web.
Last modified on 29 Jul. 2014 by andres@die.upm.es